Ocean Color Assessment of pCO2 in a River-Dominated Coastal Margin
|
Ocean Color Assessment of pCO2 in a River-Dominated Coastal Margin |
Sponsoring Agency: |
NASA |
|
|
Oceanography Program |
|
|
Office of Earth Science |
Principal Investigators: |
Steven E. Lohrenz and Wei-Jun Cai |
Project Nos.: |
NNG04GA02G |
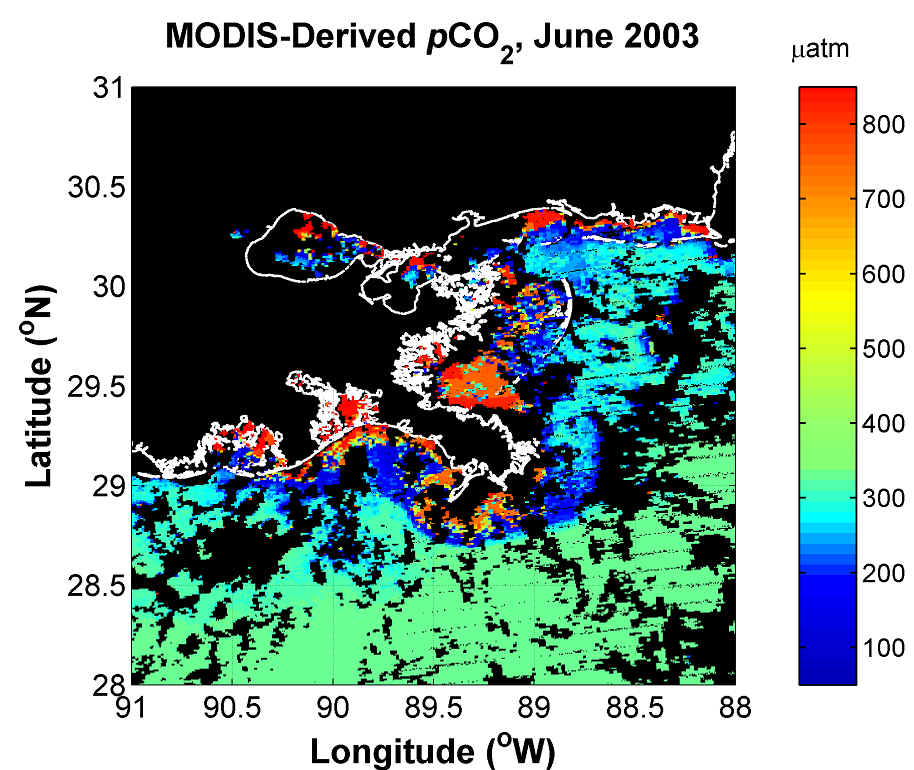
Global assessments of the oceanic carbon cycle have not fully accounted for carbon processes occurring at coastal margins. Recent measurements suggest that margins affected by large river plumes may act as a significant sink of CO2 from the atmosphere. However, quantification of the contributions of river-influenced margins to regional CO2 fluxes is difficult due to the high degree of spatial and temporal variability in these regions. We have successfully developed and applied an algorithm for assessment of areal distributions of surface water partial pressure of CO2 (pCO2) from MODIS imagery in the northern Gulf of Mexico. This algorithm was derived from relationships of in situ measurements of surface pCO2 to environmental variables (T, S, chlorophyll). We applied principal component analysis to the T, S and chlorophyll data and regressed the derived orthogonal components against pCO2. The component loadings and regression coefficients could then be used to estimate pCO2 from T, S and chlorophyll data. To derive estimates of pCO2 from the satellite imagery, products for T, S and chlorophyll were required. MODIS-Aqua L1B data were processed using SeaDAS v4.5 and sea-surface temperature (SST), chlorophyll (OC4 algorithm) and dissolved/detrital absorption (Garver-Siegel-Maritorena version 1, acdm_gsm01) products were retrieved. To provide an estimate of salinity, we used relationships between CDOM absorption (aCDOM>) and salinity for the Mississippi delta region. The algorithm to predict pCO2 from T, S and chlorophyll was applied using the MODIS-derived products to generate regional distributions of pCO2. An area of low pCO2 was evident in the vicinity of the Mississippi River delta, consistent with in situ observations. Match-up between neighboring pixels and contemporaneous in situ observations revealed good agreement, although satellite-derived estimates showed a slight positive bias. The satellite-derived assessments of pCO2 can subsequently be used in conjunction with estimates of wind fields to produce regional-scale estimates of air-sea fluxes of CO2.
Overall hypothesis: Large river margin water columns are net sinks for atmospheric carbon, but with large seasonal and spatial variability in air-sea CO2 fluxes. Such extreme variability necessitates a regional-scale assessment, such as can be achieved with satellite imagery, to accurately characterize spatially- and temporally-integrated air-sea fluxes of CO2.
Specific
Hypothesis 1:
Strong spatial gradients in air-sea fluxes of CO2 occur in
large river margins due to spatially varying effects of mixing (DT,
DS)
of river and ocean water (solubility pump), and varying intensity of the
biological pump on surface water pCO2.
Specific Hypothesis 2: Air-sea fluxes of CO2 in large river margins exhibit strong seasonal variation described by the following:
i high net uptake of CO2 in spring and early summer driven by a strong biological pump (high P/R);
ii low net uptake of CO2 in late summer and fall due to reduced river discharge, limited plume impact; and low P/R ratios; and
iii moderate net uptake of CO2 in winter and early spring in near- and mid-field dominated by a strong solubility pump due to low river temperatures and wind-driven mixing; low light conditions and deeper mixing result in a weakened biological pump during this period.
Publications
Lohrenz, S. E., Fahnenstiel, G. L., Schofield, O., and Millie, D. F. (2008) Coastal sediment dynamics and river discharge as key factors influencing coastal ecosystem productivity in southeastern Lake Michigan. Oceanography 21:60-69.
Lohrenz, S. E., D. G. Redalje, Wei-Jun Cai, J. Acker, and M. Dagg (2008) A retrospective analysis of nutrients and phytoplankton productivity in the Mississippi River Plume, Continental Shelf Research, Continental Shelf Research , doi:10.1016/j.csr.2007.06.019.
Cai, Wei-Jun, X. Guo, C. A. Chen, M. Dai, L. Zhang, S. E. Lohrenz, W. Zhai, and Y. Wang (2008) A comparative overview of weathering intensity and HCO3 - flux in the world's largest rivers, with emphasis on the Changjiang, Huanghe, Pearl and Mississippi Rivers, Continental Shelf Research , doi:10.1016/j.csr.2007.10.014 .
Green, R., G. Breed, M. Dagg, and S. E. Lohrenz (2008) Modeling planktonic dynamics and response to variable nitrate loading in the Mississippi River plume, Continental Shelf Research, doi:10.1016/j.csr.2007.02.008. .
Cai, W. J., S. E. Lohrenz, (2007) Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Fluxes from the Mississippi River and the Transformation and Fate of Biological Elements in the River Plume and the Adjacent Margin, In: Carbon and nutrient fluxes in continental margins: a global synthesis (K. K. Liu, L. Atkinson, R. Quinones and L. Talaue-McManus, Eds.), Springer-Verlag, NY.
Dagg, M.J., Ammerman, J.W., Amon, R.M.W., Gardner, W.S., Green, R.E., Lohrenz, S.E., 2007. A review of water column processes influencing hypoxia in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Estuaries and Coasts 30 (5), 735-752.
Cai, W.-J., M. Dai, and Y. Wang (2006) Air-sea exchange of carbon dioxide in ocean margins: A province-based synthesis. Geophysical Research Letters, 33, L12603, doi:10.1029/2006GL026219.
Lohrenz, S. E., and W. J. Cai (2006), Satellite ocean color assessment of air-sea fluxes of CO2 in a river-dominated coastal margin, Geophys. Res. Lett., 33, doi:10.1029/2005GL023942.
Presentations (*indicates student participation)
Lohrenz, S. E., W.-J. Cai, X. Chen, M. Tuel, Characterizing water mass properties in river dominated coastal waters using underway hyperspectral remote sensing reflectance, 6-10 October 2008, Barga, Italy (poster, contributed).
*Lohrenz, S. E., W.-J. Cai, X. Guo, S. Chakraborty, and M. Tuel, A seasonal CO2 sink associated with the Mississippi and Atchafalaya Rivers, American Geophysical Union Fall 2008 Meeting, 15-19 December 2008, San Francisco, CA.
*Cai, W.-J., X. Guo, W.-J. Huang, Y. Wang, F. Chen, M. C. Murrell, and S. E. Lohrenz, CO2 dynamics and community metabolism in the Mississippi River plume, American Geophysical Union Fall 2008 Meeting, 15-19 December 2008, San Francisco, CA.
*Lohrenz, S. E., W.-J. Cai, F. Chen, S. Chakraborty, and M. Tuel, A seasonal CO2 sink associated with the Mississippi and Atchafalaya Rivers. Ocean Carbon and Biogeochemistry Workshop, Woods Hole, MA, 21-24 July 2008 (poster, contributed).
*Cai, W.-J., X. Gao, F. Chen, W.-J. Huang, Y. Wang, and S. E. Lohrenz, The dynamics of CO2 in the Mississippi River plume and northern Gulf of Mexico, Ocean Carbon and Biogeochemistry Scoping Workshop on Terrestrial and Coastal Carbon Fluxes in the Gulf of Mexico, St. Petersburg, FL, 6-8 May 2008 (poster, contributed).
*Lohrenz, S. E., W.-J. Cai, F. Chen, X. Chen, and M. Tuel, Variability in satellite algorithms for regional assessments of pCO2, Ocean Carbon and Biogeochemistry Scoping Workshop on Terrestrial and Coastal Carbon Fluxes in the Gulf of Mexico, St. Petersburg, FL, 6-8 May 2008 (poster, contributed).
Lohrenz, S. E., Gulf of Mexico Carbon Cycling, Ocean Carbon and Biogeochemistry Scoping Workshop on Terrestrial and Coastal Carbon Fluxes in the Gulf of Mexico, St. Petersburg, FL, 6-8 May 2008 (oral, invited).
Lohrenz, S. E., O. M. E. Schofield, G. L. Fahnenstiel, D. F. Millie, Optical characterization of physical and biogeochemical variability in a Lake Michigan coastal ecosystem, ASLO, AGU, TOS Ocean Sciences Meeting, Orlando, FL, 3-7 March, 2008 (oral, contributed).
Lohrenz, S. E., D. G. Redalje, and W. –J. Cai, Temporal Relationships Between Riverine Nutrient Inputs and Phytoplankton Biomass and Productivity in the Mississippi River Plume, Estuarine Research Federation Meeting, Providence, RI, November 5-8, 2007.
Tuel, Merritt, S. E. Lohrenz and D. G. Redalje, The USM method, NASA HPLC Pigment Analysis Workshop, Copenhagen, Denmark, October 22-25, 2007.
Lohrenz, S., Stephan Howden, Wei-Jun Cai, Xiaogang Chen, and Merritt Tuel (invited), Satellite and in situ optical assessments of environmental responses to Hurricanes Katrina and Rita in coastal waters of the northern Gulf of Mexico, University of South Caroline – Columbia, August 31, 2007.
Lohrenz, S. E., W.-J. Cai, F. Chen, X. Chen, and M. Tuel, Examining Distributions and Controlling Mechanisms of pCO2 and Air-Sea Fluxes of CO2 in the Northern Gulf of Mexico, Ocean Carbon and Biogeochemistry Workshop, Woods Hole, MA, July 23-26, 2007.
Lohrenz, S. E., Northern Gulf Institute: USM Led Efforts, Northern Gulf Institute PI Workshop, 16-17 May 2007.
Lohrenz, S. E., W.-J. Cai, F. Chen, X. Chen, and M. Tuel, Seasonal variability in air-sea fluxes of CO2 in a river-influenced coastal margin, NASA Ocean Color Research Team Meeting, Seattle, WA, 11-13 April, 2007.
*W.-J. Cai, X. Gao, and S. E. Lohrenz, F. Chen, Y. Wang, Surface water CO2 study in the Mississippi River Plume and Northern Gulf of Mexico, SOLAS Open Science Conference, March 6-9, 2007, Xiamen, China.
*Lohrenz, S. E., W.-J. Cai, F. Chen, X. Chen, and M. Tuel, Seasonal dynamics in satellite-derived air-sea fluxes of CO2 in a river-influenced coastal margin, American Society of Limnology and Oceanography Aquatic Sciences Meeting, Santa Fe, NM, 4-9 Feburary 2007.
*Lohrenz, S. E., W.-J. Cai, F. Chen, X. Chen, and M. Tuel, Seasonal variability in air-sea fluxes of CO2 in a river-influenced coastal margin, U.S. North American Carbon Program (NACP) Investigators Meeting, Colorado Springs, CO, January 22-26, 2007.
Cai, W.-J., S. E. Lohrenz, and R. Wanninkhof, Air-sea CO2 flux and carbon budget in the Gulf of Mexico: State of knowledge and research initiatives in North America’s largest marginal sea, U.S. North American Carbon Program (NACP) Investigators Meeting, Colorado Springs, CO, January 22-26, 2007.
Lohrenz, S. E. (invited), Biogeochemical and Ecosystem Processes in a River-Dominated Margin, Texas A&M Galveston, Galveston, TX, 7 February 2006.
Lohrenz, S. E., and W.-J. Cai, Satellite Assessments of Air-Sea Fluxes of CO2 in a River-Dominated Coastal Margin, Ocean Carbon and Biogeochemistry Workshop, Woods Hole, MA, July 23-26, 2006.
Lohrenz, S. E., W.-J. Cai, X. Chen, M. Tuel, and F. Chen, Assessment of River Margin Air-Sea CO2 Fluxes, NASA Ocean Color Research Team Meeting, Newport, RI, 11-13 April, 2006.
Lohrenz, S. E., X. Chen, and M. Tuel, Underway Determinations of Hyperspectral Visible and Discrete UV Remote Sensing Reflectance in Optically Complex Coastal Waters, Ocean Optics XVIII, Montreal, Quebec, 9-13 October, 2006.
*Lohrenz, S. E., Cai, W.-J., Chen, X. Tuel, M., and Chen, F., Satellite Assessments of Air-Sea Fluxes of CO2 in a River-Dominated Coastal Margin, Ocean Carbon and Biogeochemistry Workshop, July 10-14, 2006, Woods Hole, MA.
*Lohrenz, S. E., Cai, W.-J., Chen, X. Tuel, M., and Chen, F., Assessment of River Margin Air-Sea CO2 Fluxes, NASA Ocean Color Research Team meeting, April 11-13, 2006, Providence, RI.
*Lohrenz, S. E., W. J. Cai, and V. Wright, 2004. Satellite Ocean Color Assessment of pCO2 in a River-Dominated Coastal Margin, Ocean Optics XVII, Fremantle, Australia, October 25-29, 2004.
Lohrenz, S. E., Cai, W. J., Satellite-Aided Estimation of Air-Sea Fluxes Of CO2 in a River-Dominated Coastal Margin, ASLO Aquatic Sciences Meeting, Salt Lake City, 20-25 February 2005.